It turns out that the first two weeks were terrible.
The United States has just broken its historical records for most Covid-19 infections, hospitalizations and deaths reported in one day:
– On January 2, a record 302,506 new infections were reported in one day, according to Johns Hopkins University.
That’s an average of 3.5 people being infected every second.
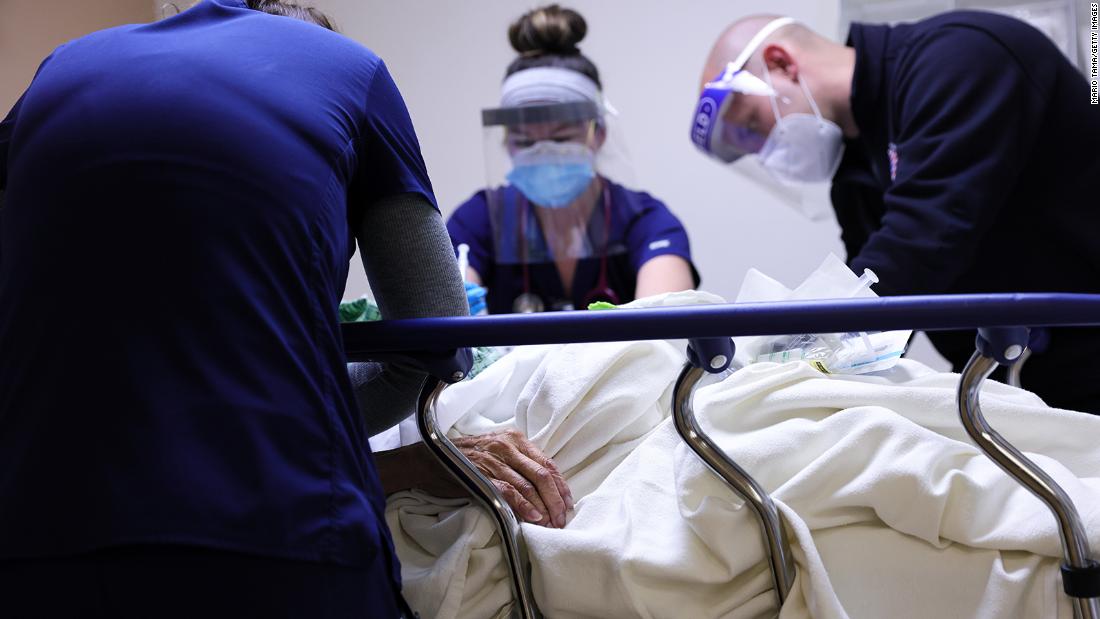
– On January 6, a record 132,447 patients were hospitalized with Covid-19, according to the Covid Tracking Project.
Many hospitals are now overcrowded, which means that even those without Covid-19 – say, victims of car accidents – may not receive immediate care.
– On January 12, a record 4,462 Covid-19 deaths were reported in just one day, according to Johns Hopkins.
Why is this happening?
“If you go to a party with five or more people, there will almost certainly be someone with Covid-19 at that party,” said Dr. Peter Hotez, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine.
One reason the coronavirus spreads so easily is because people can be contagious without knowing they are infected – and they can transmit the virus without looking or feeling bad.
“This means that at least half of the new infections come from people who are probably unaware that they are infectious to others,” the agency said.
The consequences of the holidays may still spread across the United States in the coming weeks.
“It takes two to three weeks for patients to be sick enough to need the hospital after they have contracted the virus,” said Dr. Anish Mahajan, medical director at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center.
Although Christmas was less than three weeks ago, “we are already full”.
“We no longer have the capacity in the ICU,” said Mahajan. “All hospitals in the region are placing ICU patients in unusual places in the hospital just to find space for them.”
So, there are newly identified variants
These cases in the U.S. have been found in 12 states: California, Florida, Minnesota, New York, Colorado, Connecticut, Maryland, Texas, Pennsylvania, Indiana, Wisconsin and Georgia, according to CDC data published on Wednesday.
Understanding the genetic makeup of a virus and how it changes is critical to ensuring that vaccines remain effective.
All viruses mutate over time and new variants are common.
While it may be more transmissible, there is no evidence that this variant first detected in the UK is more deadly or causes more serious illness, said the CDC.
But the strain first detected in the UK is not the only one that causes concern.
This strain was first detected two months ago in South Africa and was found in 12 countries. Until Thursday, it had not been detected in the United States.
Why can’t we all get vaccinated soon?
As of Thursday morning, about 10.2 million doses of vaccine were administered, out of about 29.3 million doses distributed in the United States, according to the CDC.
And the two vaccines now distributed in the United States – from Pfizer / BioNTech and Moderna – require two doses for each person.
But in any case, millions of Americans will have to wait months before receiving a vaccine.
What does all this mean for you
If you want to get life closer to normal (and faster), it’s time to double the security measures:
Keep social distance. Wash your hands frequently. And don’t think that you are invincible – even if you are young and healthy.
“Whether due to … a higher dose of the virus, if they have genetic changes that they don’t know about – we just don’t understand,” he said.
“Therefore, we cannot safely predict who will handle this virus well and who will not.”
Elizabeth Cohen, Maggie Fox, Michael Nedelman and Amanda Watts of CNN contributed to this report.