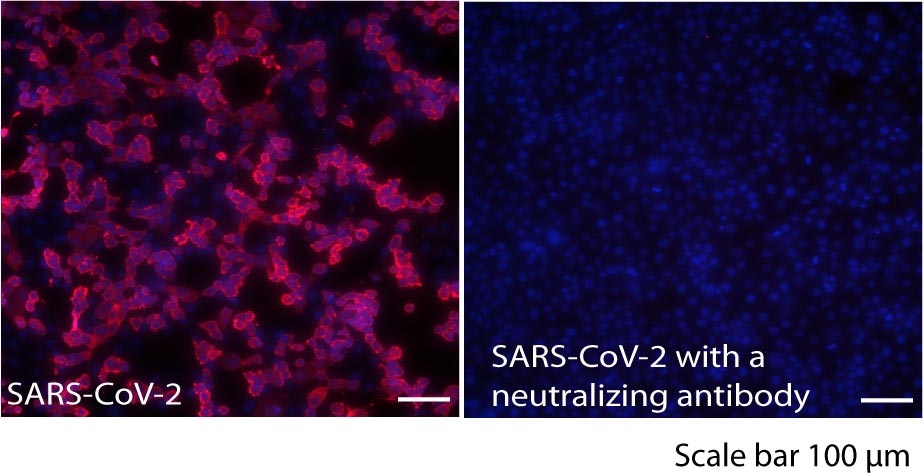
SARS-CoV-2 infected untreated Vero cells (left) and treated with neutralizing antibody (right). Credit: Mor M, et al., 2021, PLOS Pathogens, CC BY 4.0
The majority of the population can produce neutralizing antibodies against coronavirus 2 of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2) in severe cases of coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19), according to a study published today (11 February 2021) in the open access newspaper PLOS Pathogens by Michael Mor of Tel Aviv University, and colleagues. In addition, the results support the use of combined antibody therapy to prevent and treat COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has had a profound impact on global public health. Neutralizing antibodies that specifically target the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) are believed to be essential for virus control. Neutralizing antibodies specific to RBD have been detected in convalescent patients – those who have recovered from COVID-19. Some of those recovered tend to have robust and long-lasting immunity, while others exhibit a decrease in their neutralizing antibodies. The factors associated with an effective and durable antibody response are still unclear.
To address this knowledge gap, Mor and colleagues used molecular and bioinformatics techniques to compare B cell responses in eight patients with severe COVID-19 and 10 subjects with mild symptoms, 1.5 months after infection. Very sick patients showed higher concentrations of RBD-specific antibodies and increased B-cell expansion. Among 22 cloned antibodies from two of these patients, six exhibited potent neutralization against SARS-CoV-2.
Bioinformatics analysis suggests that most people would be able to readily produce neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in severe cases of COVID-19. In addition, combinations of different types of neutralizing antibodies have completely blocked the spread of the live virus. According to the authors, these antibody cocktails can be tested in clinical settings as a useful means of preventing and treating COVID-19.
“Even with a vaccine at our doorstep, arming doctors with specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapy is extremely important,” add the authors. “Combinations of neutralizing antibodies represent a promising approach for the effective and safe treatment of severe cases of COVID-19, especially in the elderly population or people with chronic diseases, who will not be able to produce these antibodies as easily after infection or vaccination. “
Reference: “SARS-CoV-2 multi-clonal neutralization by antibodies isolated from serious COVID-19 convalescent donors” by Mor M, Werbner M, Alter J, Safra M, Chomsky E, Lee JC, et al., February 11, 2021, PLOS Pathogens.
DOI: 10.
Funding: This research was funded by grant 3711/20 from the Israel Science Foundation (NTF) and by the Vice President of Research and Development at Tel Aviv University. NTF is also funded by ISF grant number 41222/18 and Israel Innovation Authority 68972. This work was also supported by NIH Grant RO1 HL124209 (BC), American Asthma Foundation (BC) and BSF 2017176 (BC) and a career award for medical scientists from the Burroughs Welcome Fund (AFC). Funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.